Discovering Cyclohexane: The Invisible Powerhouse Behind Your Favorite Products
Hey there, chemistry enthusiasts and curious minds! Ever wondered about the hidden ingredients that make up the stuff we use every day? Enter cyclohexane – a simple, ring-shaped molecule that's quietly revolutionizing industries from fashion to fuel. With the formula C₆H₁₂, this colorless, flammable liquid is like the reliable sidekick in a superhero movie: not always in the spotlight, but essential for the big wins. Let's dive into what makes cyclohexane tick, from its quirky structure to its real-world superpowers, and keeping things safe and sustainable.
What Makes Cyclohexane So Special? A Quick Look at Its Basics
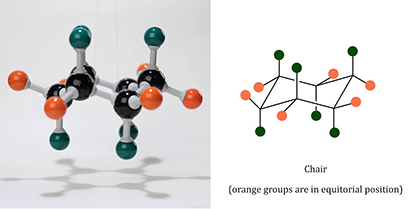 Picture cyclohexane as a cozy circle of six carbon atoms, each holding hands with two hydrogen buddies. This setup forms a stable ring, but it's not flat like a pancake – it twists into a "chair" shape to avoid any awkward bumps or strains, kind of like how you adjust your seat for maximum comfort during a long movie.
Picture cyclohexane as a cozy circle of six carbon atoms, each holding hands with two hydrogen buddies. This setup forms a stable ring, but it's not flat like a pancake – it twists into a "chair" shape to avoid any awkward bumps or strains, kind of like how you adjust your seat for maximum comfort during a long movie.
At room temperature, it's a clear liquid that's easy to handle: it melts at about 6.5°C (just above freezing water) and boils at 80.7°C (hotter than a summer day). Weighing in at 84.16 grams per mole, with a density lighter than water (0.7781 g/cm³ at 20°C), it floats on top if you try mixing them – which you can't really, since it's insoluble in water but buddies up with other organic solvents like ethanol or ether.
Physically, it's got low stickiness (viscosity) and spreads easily, making it great for sneaking into tight spots, like swelling rubber without much fuss.
Chemically, cyclohexane is a tough cookie thanks to its ring design – more stable than straight-line cousins like hexane. It doesn't react easily at normal temps, but crank up the heat or add a catalyst, and it can transform:
Halogenation: With light or help from a catalyst, it swaps hydrogens for halogens like chlorine, creating useful derivatives.
Dehydrogenation: Heat it over 300°C with platinum or palladium, and it sheds hydrogens to become benzene – like a caterpillar turning into a butterfly.
Oxidation: Mix with air, and it becomes cyclohexanone or cyclohexanol, key steps in making.
Where Does Cyclohexane Show Up in Your Life?
Cyclohexane isn't just lab stuff – it's a workhorse in everyday products.:
As a Super Solvent
Need to thin out paint, glue rubber parts, or extract oils? Cyclohexane's your go-to. It dissolves resins, coatings, and fats like a champ, and about 35% of the world's supply goes into solvents. The best part? It's a greener swap for benzene, which is super toxic – benzene can cause serious health issues like leukemia with long exposure. By using cyclohexane instead, industries cut down on harmful fumes, protecting workers and the planet during degreasing, cleaning, or paint-stripping jobs. For example, in the production of paint thinners, adhesives, and even video and audio tape cleaners, cyclohexane has been widely adopted as a safer alternative, reducing the risk of chronic health issues associated with benzene exposure.
The Backbone of Nylon
This is where cyclohexane shines brightest. It's the starting point for making nylon, especially nylon 66, with over 6 million tons  produced globally each year. Think about it: that tough carpet fiber under your feet, the lightweight parts making your car more fuel-efficient, or the durable outdoor apparel keeping you dry on a hike – all trace back to cyclohexane.
produced globally each year. Think about it: that tough carpet fiber under your feet, the lightweight parts making your car more fuel-efficient, or the durable outdoor apparel keeping you dry on a hike – all trace back to cyclohexane.
How? It gets oxidized into cyclohexanone and cyclohexanol, then transformed into adipic acid and caprolactam, the building blocks of nylon. Without cyclohexane, your wardrobe and home would feel a lot less comfy!
Boosting Fuels and More
Mixed into gasoline, cyclohexane bumps up the octane rating, helping engines run smoother without knocking – all while meeting strict environmental standards like ASTM D4814. In labs, it's a trusty solvent for chromatography (separating mixtures) or a standard in experiments. It even helps synthesize other compounds, keeping research rolling.
How Is Cyclohexane Made? From Oil to Ring
Most cyclohexane comes from two main paths:
Petroleum Cracking: Straight from oil fractions – cheap and cheerful, but not super pure, so it's perfect for solvent gigs.
Benzene Catalytic Hydrogenation: The big player! Benzene (a ring-shaped molecule from petrochemical refining of crude oil) reacts with hydrogen at 200-300°C under pressure (1-3 MPa), with a nickel catalyst speeding things along. Yield? Up to 95%. This gives a full picture: oil gets refined into benzene, which then "hugs" hydrogen to become cyclohexane – a seamless supply chain from earth to factory.
Staying Safe with Cyclohexane
Sure, it's useful, but cyclohexane is flammable (Category 2) and can be a health hazard (Category 3) if mishandled. Store it in cool, dark, explosion-proof spots below 30°C, far from oxidizers. If it spills, soak it up with activated carbon or diatomaceous earth – no water rinses allowed, as that could spread the fire risk.
Gear up with nitrile gloves and a proper gas mask to avoid skin irritation or breathing in vapors. Safety first keeps this hero from turning villain!
The Future of Cyclohexane: Growing Greener
 Demand's booming at 4.2% yearly, thanks to nylon's role in lighter cars and tech gadgets. But the industry's eyeing sustainability: new bio-based methods could cut carbon footprints, making cyclohexane even more eco-friendly. As we push for decarbonization, optimizing production and minimizing waste will keep this compound central to a brighter, chemical-savvy world.
Demand's booming at 4.2% yearly, thanks to nylon's role in lighter cars and tech gadgets. But the industry's eyeing sustainability: new bio-based methods could cut carbon footprints, making cyclohexane even more eco-friendly. As we push for decarbonization, optimizing production and minimizing waste will keep this compound central to a brighter, chemical-savvy world.
There you have it – cyclohexane might not be flashy, but it's the quiet force behind so much of modern life.
Looking for a reliable bulk supplier of Cyclohexane (CAS CAS 110-82-7)?
Aure Chemical provides PremiumCyclohexane (CAS CAS 110-82-7) raw materials.
View our Cyclohexane (CAS CAS 110-82-7) product page
