Aure Chemical: Your Trusted Partner for Stabilized Acrylic Acid (CAS 79-10-7)
Aure Chemical is a premier global supplier of Stabilized Acrylic Acid, also known as 2-Propenoic acid or Prop-2-enoic acid. This fundamental organic compound is highly valued for its unique reactivity, making it a cornerstone chemical in the production of countless essential materials. Our commitment to safety and quality ensures we provide Acrylic Acid that is carefully inhibited against uncontrolled polymerization, guaranteeing stability and reliability for your most critical applications.
Basic Information of Acrylic Acid
Acrylic Acid (CAS No. 79-10-7) adheres to rigorous quality standards, featuring an effective polymerization inhibitor (commonly MEHQ) to ensure its safe handling and performance:
| CAS No.: | 79-10-7 |
|---|
| EC No.: | 201-177-9 |
|---|
| Linear Formula: | C₃H₄O₂ |
|---|
| Molecular Weight: | 72.06 |
|---|
| Appearance: | Colorless liquid (often referred to as Glacial Acrylic Acid for high-purity form) |
|---|
| Melting Point: | 14 °C |
|---|
| Boiling point | 141 °C |
|---|
| Density: | 1.05 g/mL at 20 °C |
|---|
| Solubility: | Miscible with water, alcohol, ether, and most organic solvents. |
|---|
| Flash Point: | 130 °F |
|---|
| Purity: | Corrosive liquid, flammable (combustible), contains a polymerization inhibitor. |
|---|
| RIDADR: | UN 2218 8/PG 2 |
|---|
| Chemical Structure: | 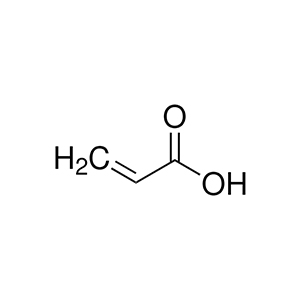 |
|---|
Our product’s consistent purity and carefully controlled stability make it ideal for demanding industrial processes.
Why the "Stabilized" Aspect of Acrylic Acid is Paramount
The emphasis on the "stabilized" nature of Acrylic Acid is not merely a quality feature; it's a critical safety requirement. Acrylic Acid possesses an inherent and strong tendency to polymerize, which can lead to hazardous situations if not properly managed:
Risk of Uncontrolled Polymerization:
Polymerization is a highly exothermic (heat-releasing) reaction. If this reaction occurs uncontrollably within a container, the rapidly generated heat can cause a dangerous increase in temperature and pressure. This can lead to the container rupturing violently or even exploding, releasing hot, corrosive, and flammable Acrylic Acid and its vapors, posing severe risks of fire, chemical burns, and environmental contamination.
Factors Triggering Instability:
Even with stabilizers, certain conditions can compromise Acrylic Acid’s stability and initiate uncontrolled polymerization:
Elevated Temperatures: Excessive heat can override the inhibitor's effectiveness.
Contamination: Trace impurities, especially metal ions (like iron or copper), strong acids, strong bases, or free radical initiators, can act as catalysts.
Loss of Inhibitor Effectiveness: The inhibitor (e.g., MEHQ) requires the continuous presence of oxygen (usually air) to function properly. Storage under an inert atmosphere or oxygen depletion can render it ineffective.
Freezing and Improper Thawing: If the acid freezes, the inhibitor may separate. Improper thawing (e.g., localized heating) can lead to polymerization in uninhibited areas.
Aure Chemical's Commitment to Stability:
We ensure our Acrylic Acid is properly inhibited and provide clear guidelines for storage and handling, requiring temperature control and appropriate oxygen exposure to maintain stability throughout its shelf life and transport.
Application of Acrylic Acid
The controlled reactivity of stabilized Acrylic Acid, combined with its ability to form long polymer chains, makes it indispensable across diverse industries:
Superabsorbent Polymers (SAPs):
The single largest application of Acrylic Acid is in the production of Superabsorbent Polymers (SAPs). These polymers can absorb and retain extremely large amounts of liquid relative to their own mass, making them essential components in disposable diapers, adult incontinence products, and feminine hygiene products.
Coatings, Adhesives, and Sealants:
Acrylic Acid is a key monomer in the production of acrylic polymers and copolymers used in various high-performance coatings, adhesives, and sealants. These products offer excellent adhesion, weatherability, color retention, and flexibility.
Thickeners and Dispersants:
Polyacrylates derived from Acrylic Acid serve as effective thickeners, dispersants, and rheology modifiers in applications ranging from paints and detergents to cosmetics and oilfield chemicals.
Flocculants and Water Treatment Chemicals:
Polymers based on Acrylic Acid are widely used as flocculants in water treatment processes, helping to clarify water by causing suspended particles to clump together.
Other Chemical Intermediates:
It acts as a versatile chemical intermediate for the synthesis of esters (acrylates), which are then used in the production of specialty polymers and various chemical products, including certain plasticizers and chemical auxiliaries.
Why Choose Aure Chemical for Your Stabilized Acrylic Acid Supply?
Aure Chemical is dedicated to providing superior chemical solutions and unmatched customer support. By partnering with us for your Stabilized Acrylic Acid requirements, you benefit from:
Guaranteed Purity & Stability: Our Acrylic Acid is manufactured and tested to strict specifications, ensuring high purity and effective stabilization crucial for your sensitive processes.
Reliable & Safe Supply Chain: We maintain a robust and compliant global supply chain, guaranteeing the safe, timely, and secure delivery of this critical chemical to your facilities worldwide.
Expert Technical Support: Our team of experienced chemists and specialists is readily available to offer comprehensive guidance on product application, safe handling, and optimal storage conditions to maintain stability.
Commitment to Quality & Safety: We adhere to the highest industry standards for quality management, safety, and environmental responsibility, from manufacturing to distribution.
Choose Aure Chemical for a trustworthy and dependable supply of high-quality Stabilized Acrylic Acid. We are ready to support your most complex and innovative chemical projects.
Hazards Classification
GHS Classification: Flammable Liquid (GHS02), Corrosive (GHS05), Acute Toxicity (GHS06), Environmental Hazard (GHS09)
Hazard Statements: Flammable liquid and vapor; causes severe skin burns and eye damage; harmful if swallowed, in contact with skin, or if inhaled; toxic to aquatic life with long lasting effects.
UN Number: UN 2218
Hazard Class: 8 (Corrosive Substances), 3 (Flammable Liquids)
Packing Group: II
 GHS02: Flammable
GHS02: Flammable GHS05: Corrosive
GHS05: Corrosive GHS06: Acute Toxicity
GHS06: Acute Toxicity GHS09: Environmental Hazard
GHS09: Environmental Hazard
