Explore Top-Quality APBOA with Aure Chemical
2-(4-Aminophenyl)-5-aminobenzoxazole (APBOA), CAS 13676-47-6, also known as
5-Amino-2-(4-aminophenyl)benzoxazole or DAPBO, is a
heteroaromatic diamine monomer
featuring a rigid benzoxazole core and dual amine functionalities.
This structure imparts high thermal stability, mechanical strength, and
chemical resistance to derived polymers such as polyimides, supporting
advanced materials synthesis.
Basic Information of APBOA
| Product Name | 2-(4-aminophenyl)-5-aminobenzoxazole |
|---|
| Abbreviation | APBOA |
|---|
| CAS Number | 13676-47-6 |
|---|
| Molecular Formula | C13H11N3O |
|---|
| Molecular Weight | 225.25 g/mol |
|---|
| Appearance | Off-white to tan solid |
|---|
| Purity | ≥99% |
|---|
| Package | 1kg/bottle, 20kg/drum, or customized |
|---|
| Molecular Structure | 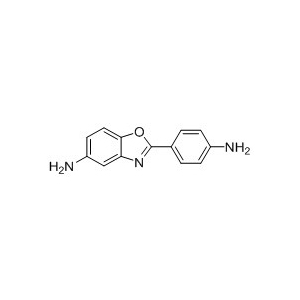 |
|---|
Key Properties
High thermal stability and structural rigidity
Good chemical resistance in harsh environments
Stable mechanical properties when incorporated in polymers
Can contribute to intrinsic flame resistance in certain polymer systems
Dual amine functionality enabling polymer chain extension or crosslinking
Key Application Contexts of APBOA
Detailed COA / TDS / MSDS are available upon request.
Please Contact Us
for more information.

